Abstract
Background: Outcomes remain dismal for patients (pts) with relapsed/refractory (R/R) AML. Programmed Death-1 (PD-1), an inhibitory receptor on T and B cells, suppresses immune activation. We hypothesized that administration of pembrolizumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting PD-1, after high dose cytarabine (HiDAC) salvage chemotherapy would stimulate a T-cell mediated anti-leukemic immune response leading to improved efficacy in R/R AML.
Methods: We are conducting a multicenter phase II study of HiDAC (<60 years: 2 gm/m2 IV Q12hours days 1-5; ≥60 years: 1.5 gm/m2 IV Q12hours days 1-5) followed by pembrolizumab 200 mg IV on day 14 in R/R AML pts 18-70 years. The primary objective of this study is to estimate the overall complete remission (CR + CRi) rate. Overall responders can receive maintenance phase pembrolizumab 200 mg IV Q3weeks for up to 2 years until progression. Allogeneic stem cell transplant (SCT) is permissible before or after maintenance phase.
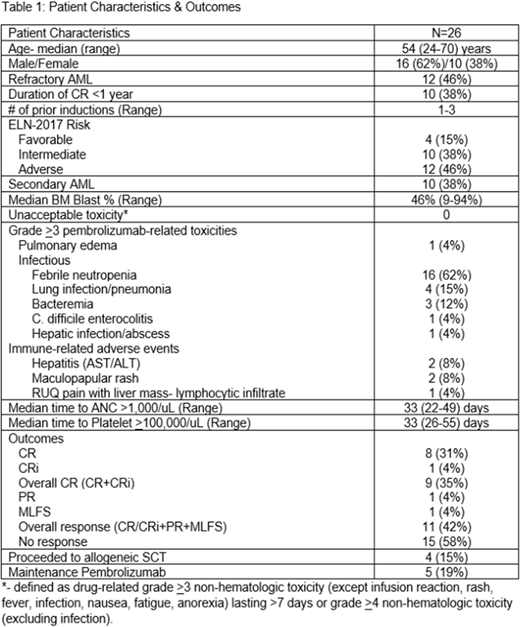
Results: To date, 26 pts are evaluable for safety and response (Table 1). Grade ≥3 immune-related adverse events have been rare and self-limiting. The overall CR rate is 35%. Of the 9 CR pts, 5 (56%) had no evidence of minimal residual disease (MRD) by standard monitoring. Notably, 2/3 primary refractory pts with inv(3) cytogenetics achieved CR and underwent SCT. Additionally, 1 pt with relapsed AML with most recent treatment refractory to HiDAC salvage achieved CR with no evidence of MRD. Five pts received maintenance pembrolizumab: 3 relapsed (median duration of CR = 2.8 months; range: 2-5.7 months), 1 proceeded to SCT after 2 cycles, and 1 initially achieved a partial remission (PR) and had stable disease for 12 cycles of maintenance pembrolizumab before progressing. Four pts received a SCT in CR (n=3) and morphologic leukemia free state (MLFS) (n=1). Grade II acute graft-versus host disease (GVHD) and moderate chronic GVHD was seen in 2/4 (50%) pts, respectively. With a median follow up of 10.8 months to date, median overall survival is 10.5 months (range: 1.8-20.8 months).
We performed B cell receptor amplicon sequencing, T cell receptor (TCR) amplicon sequencing from CD8+ T cells, and RNA-seq from enriched blasts and non-blast fractions in bone marrow (BM) from 3 CR and 3 non-responders (NR) prior to HiDAC. From the BM blast enriched fraction, expression of innate immune genes such as NLRP12, C3, S100A9, S100A12 and CD14 correlated with response. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) demonstrated that CR correlated with expression of genes in the Toll Pathway, Lysosome pathway, and adaptive immune system while NRs were associated with expression of the PAR1 and GATA3 pathways. From the non-blast BM population, CR correlated with expression of cell-cycle genes such as CCNE1, CCNB2, E2F2, KIF18B and CDKN3. Not surprisingly, GSEA revealed that expression of cell cycle pathways correlated with response. CR correlated with increased expression of B cell metagenes and the inverse IPRES signature in the non-blast BM fraction. As previously reported, there was a significant increase in peripheral blood (PB) TCR diversity in CR pts. CR was also significantly associated with the abundance and richness of the non-blast BM fraction of the B cell heavy and both light chains suggesting that a broader immune response at baseline may be critical for response to HiDAC and pembrolizumab. Finally, CR correlated with increased expression of CD300E, CCR7, CCR4, CCR8 and CCL7 in PB CD8+ T cells suggesting that migration of monocytes, T and B cells is associated with response.
Conclusions: Our findings demonstrate that pembrolizumab is well tolerated after HiDAC in an ongoing study in R/R AML. An encouraging response rate has been seen in a high-risk patient population without apparent additive toxicity post-SCT. Our RNA-seq and amplicon sequencing data indicate that biomarkers of response are present prior to therapy. Increased expression of innate immune genes expressed by leukemic blasts and cell cycle genes by the non-blast fraction correlated with response to therapy. Additionally, CR was associated with increased measures of B and T cell diversity and immune cell migration. Further immunogenomic biomarker correlates are ongoing to determine predictors of response to pembrolizumab after HiDAC in R/R AML.
Zeidner:Tolero: Honoraria, Other: Travel Fees, Research Funding; Asystbio Laboratories: Consultancy; Merck: Research Funding; Takeda: Other: Travel fees, Research Funding; Rafael Pharmaceuticals: Other: Travel Fees; Celgene: Honoraria. Vincent:Merck: Research Funding. Foster:Celgene: Research Funding; Macrogenics: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Shire: Honoraria. Coombs:Incyte: Other: Travel fees; AROG: Other: Travel fees; DAVA Oncology: Honoraria; Abbvie: Consultancy; H3 Biomedicine: Honoraria. Luznik:WIndMIL Therapeutics: Equity Ownership, Patents & Royalties. Gojo:Merck inc: Research Funding; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Research Funding; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Serody:Merck: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal